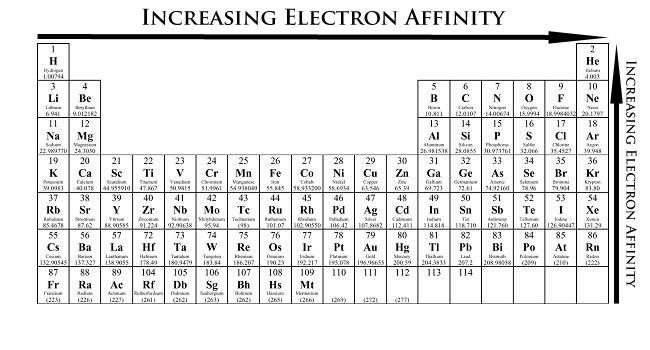
The chart shows electronegativities from sodium to chlorine - you have to ignore argon. 9th - 12th grade.
Periodic Trends Chemistry Libretexts
What is the periodic trend for electronegativity.
. Electronegativity increases as you move across the periodic table from left to right. Electron Affinity The energy released when an electron is added to a gaseous atom Ag e-1 A-1 energy The atom turns into an anion in the process The process for fluorine can be represented as follows. There is an increased nuclear attraction AND the.
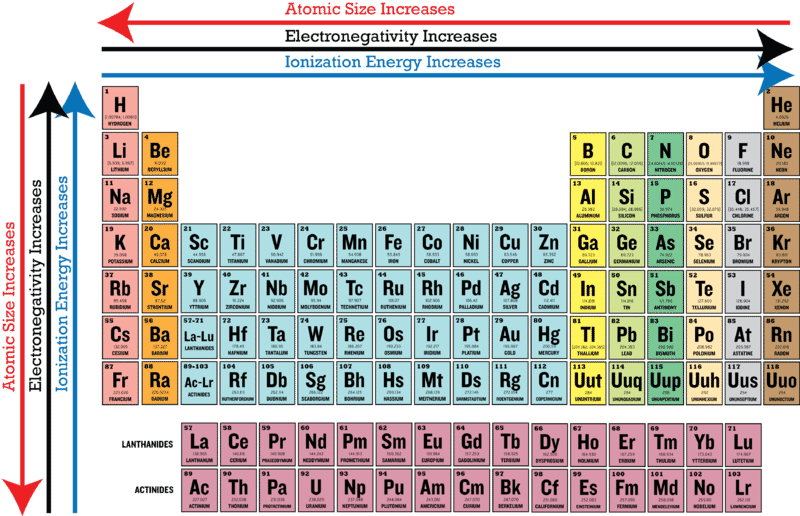
The Periodic Law states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern. As you move across a row of the periodic table there are more protons and electrons but the electrons are held more closely to the nucleus so the overall size of the atom. The Structure of an Atom.
As you go across a period the electronegativity increases. Electronegativity and the Periodic Table. Which of the following trends is similar to electronegativity follows the same pattern.
Fluorine is the most electronegative element. In general electronegativities decrease down a Group of the Periodic Table. Periodic Table Trends.
The overall trend for electronegativity in the periodic table is diagonal from the lower left corner to the upper right corner. Periodic tables are the patterns of the properties of chemical elements that are in the periodic table of elements. Modern Periodic Table Trends.
There are specific patterns present in the arrangement of elements in the periodic table. The Periodic Table of the Elements with Electronegativities 1 18 Hydrogen 1 H 101 21 2 Alkali metals Alkaline earth metals Transition metals Lanthanides Actinides Other metals Metalloids semi-metal Nonmetals 694 Halogens Noble gases Element name 80 Symbol Beryllium Electronegativity Mercury Hg 20059 19 Atomic Lithium Avg. It comes as no surprise that fluorine is the undisputed king of electronegativity.
In the real world where atoms are far more commonly found chemically bonded to other atoms electronegativity gives us a more usable measure of how a tug-of-war for electrons between atoms plays out. We can see this with the help of a graph showing the trend in electronegativity in period 3 from sodium to chlorine. Following this pattern cesium is shown to have the largest atomic radius.
It doesnt have an electronegativity because it doesnt form bonds. For example the format of the periodic table is designed so properties can be easily compared. Electronegativity values generally increase from left to right across the periodic table.
The highest electronegativity value is for fluorine. Studying these trends allows chemists scientists and even us to quickly identify certain properties of an element. Lithium 10 and Fluorine 40 in period 2.
In this graph we have not shown argon as it does not react with elements to form bonds. Increases as you move left to right across a period. Trends in electronegativity down a group.
How to Read the Periodic Table. Define the following termsstarting on page 170. Trends in electronegativity across a period.
These arise from the changes in the atomic. Pauling devised a numerical electronegativity scale based on bond energies. What is the periodic trend for electronegativity.
These periodic table trends arise out of the specific arrangement of elements due to the Periodic Law. The Periodic Table is arranged according to the Periodic Law. As you move from left to right across the periodic table electronegativity increases and as you move down the table electronegativity decreases.
Mass 13 14 15 16 17. For example the electronegativity trend across period 3 in the periodic table is depicted below. There are certain trends and patterns in the way elements react and behave.
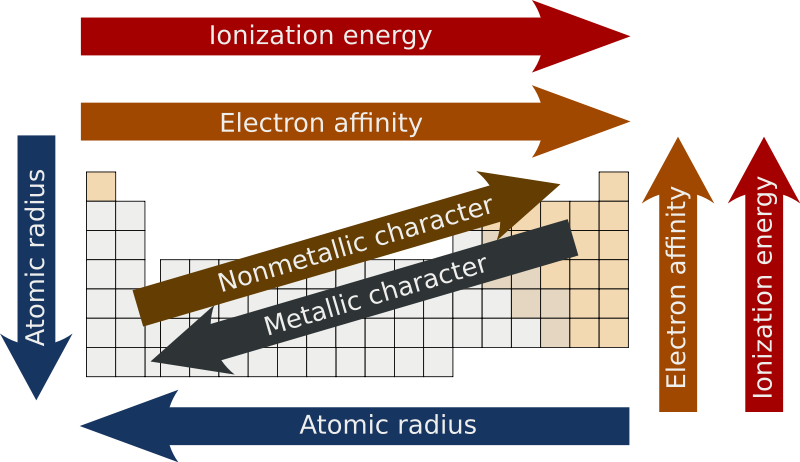
Mainly it includes electronegativity ionization energy electron affinity atomic radii ionic radius metallic character and chemical reactivity. As we move across a period from left to right the nuclear charge increases and the atomic size decreases therefore the value of electronegativity increases across a period in the modern periodic table. Read on to know more.
Trends and Pattern of Periodic Table. Atomic radius- First ionization energy-Electronegativity-. The trend closely resembles electronegativity.
Lithium 10 and Francium 07 in Group I. In general electronegativities increase going from left to right across a Period of the Periodic Table. Electronegativities generally decrease from top to bottom of a group.
As you go down a group electronegativity decreases. When we move from left to right in a period of the modern periodic table electronegativity increases. Periodic Trends in the Electronegativities of Elements.
Since the electronegativity of some of. Through Periodic trends the atomic radius increases in size further left of a period and lower down a group. The electronegativity also increases up a group column of the periodic table.
Trends in electronegativity across a period. Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom to attract the electrons when the atom is part of a compound. F g e- F- g energy Trends in EA Across a period.
This occurs due to a greater charge on the nucleus causing the electron bonding pairs to be very attracted to atoms placed further right on the periodic table. This trend in properties is known as periodic properties. The trends for electronegativity is that the value increases across the periods rows of the periodic table.
The atomic number of the elements on the periodic table are organized chronologically starting with Hydrogen with the the atomic number of 1 going from left to right. 120 rows We observe a common trend in properties as we move across a period from left to right or down the group. These related values display the same trend in the periodic table.
As you move from left to right across the periodic table electronegativity increases and as you move down the table electronegativity decreases. The important periodic properties are atomic size metallic character non-metallic character ionization potential electron affinity and electronegativity. Increasing e- affinity Reason.
As you move down the periodic table elements have more protons and gain an electron energy shell so atoms become larger.

Electronegativity Definition And Trend
Periodic Trends In Electronegativity Ck 12 Foundation
What Trend In Electronegativity Do You See As You Go Across A Period Row On The Periodic Table Socratic

Periodic Trends In Electronegativity Ck 12 Foundation

Periodic Trends Made Easy Chemtalk

What Is Electronegativity Trends Chart Periodic Table Chemtalk

0 comments
Post a Comment